



Hydraulic vane pumps are a type of positive displacement pump commonly used in hydraulic systems to generate fluid flow. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the working principles, construction, advantages, disadvantages, and various applications of hydraulic vane pumps
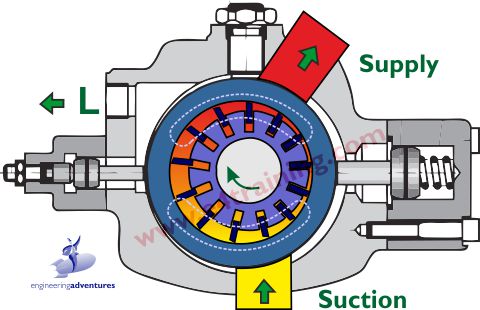
Hydraulic vane pumps operate on the principle of positive displacement, meaning they displace a fixed amount of fluid with each revolution
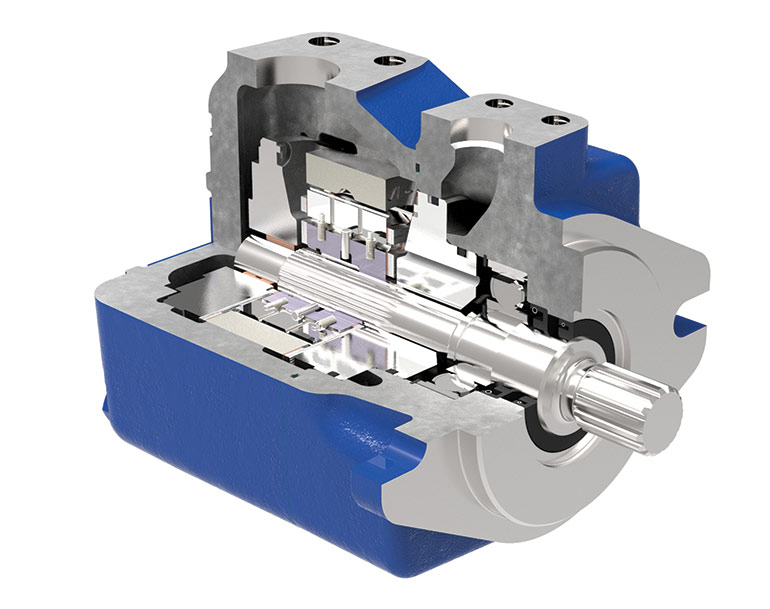
The main components include a rotor, vanes, a stator, and an inlet and outlet port.
The operation of a hydraulic vane pump can be broken down into several stages:
Hydraulic vane pumps have a relatively simple construction compared to some other types of hydraulic pumps. The key components include:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Hydraulic vane pumps find applications in various industries and systems, including:
Hydraulic vane pumps offer a reliable and efficient solution for various hydraulic applications. Their simple construction, quiet operation, and suitability for specific pressure and flow rate requirements make them a preferred choice in certain industries. However, it’s essential to consider their limitations, such as sensitivity to contaminants and pressure constraints, when selecting a pump for a particular application.